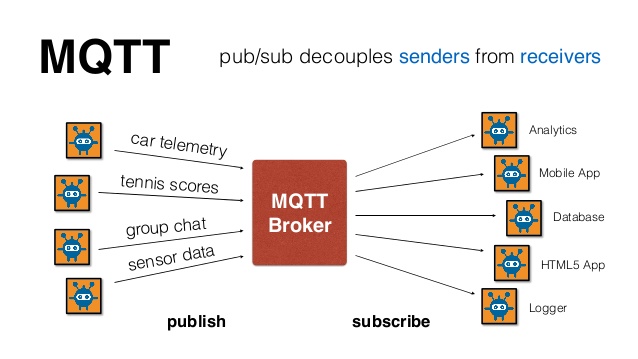
MQTT (formerly MQ Telemetry Transport) is a publish-subscribe based "light weight" messaging protocol for use on top of the TCP/IP protocol. It is designed for connections with remote locations where a "small code footprint" is required or the network bandwidth is limited. The publish-subscribe messaging pattern requires a message broker. The broker is responsible for distributing messages to interested clients based on the topic of a message. Andy Stanford-Clark and Arlen Nipper of Cirrus Link Solutions authored the first version of the protocol in 1999.
The specification does not specify the meaning of "small code foot print" or the meaning of "limited network bandwidth". Thus, the protocol's availability for use depends on the context. In 2013, IBM submitted MQTT v3.1 to the OASIS specification body with a charter that ensured only minor changes to the specification could be accepted. MQTT-SN is a variation of the main protocol aimed at embedded devices on non-TCP/IP networks, such as ZigBee.
Historically, the 'MQ' in 'MQTT' came from IBM's MQ message queuing product line. However, queuing per se is not required to be supported as a standard feature in all situations.
Alternative protocols include the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol, the IETF Constrained Application Protocol[6] and XMPP.
MQTT Broker
There are several MQTT brokers available such as ActiveMQ, Apollo, IBM Message Sight, JoramMQ, Mosquitto, RabbitMQ, and Solace Message Routers. They vary in their feature set and some of them implement additional features on top of the standard MQTT functionality. See MQTT.org for more information.
A comparative study of the performance of these different brokers (ActiveMQ, Apollo, JoramMQ, mosquitto and RabbitMQ) can be found here.
Real world applications
In the real world, there are a number of projects that implement MQTT.
- Facebook Messenger. Facebook has used aspects of MQTT in Facebook Messenger. However, it is unclear how much of MQTT is used or for what; Moreover, it is to be noted that this is a phone application, not a sensor application.
- IECC Scalable DeltaRail's latest version of their IECC Signaling Control System uses MQTT for communications within the various parts of the system and other components of the signaling system. It provides the underlying communications framework for a system that is compliant with the CENELEC standards for safety-critical communications.
- The EVRYTHNG IoT platform uses MQTT as an M2M protocol for millions of connected products.
- On October 8, 2015 Amazon Web Services announced Amazon IoT is based on MQTT.