Digital signal processing (DSP) is the numerical manipulation of signals, usually with the intention to measure, filter, produce or compress continuous analog signals. It is characterized by the use of digital signals to represent these signals as discrete time, discrete frequency, or other discrete domain signals in the form of a sequence of numbers or symbols to permit the digital processing of these signals.
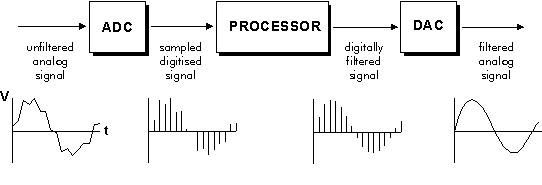
Theoretical analyses and derivations are typically performed on discrete-time signal models, created by the abstract process of sampling. Numerical methods require a digital signal, such as those produced by an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The processed result might be a frequency spectrum or a set of statistics. But often it is another digital signal that is converted back to analog form by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). Even if that whole sequence is more complex than analog processing and has a discrete value range, the application of computational power to signal processing allows for many advantages over analog processing in many applications, such as error detection and correction in transmission as well as data compression.
Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing. DSP applications include audio and speech signal processing, sonar and radar signal processing, sensor array processing, spectral estimation, statistical signal processing, digital image processing, signal processing for communications, control of systems, biomedical signal processing, seismic data processing, among others. DSP algorithms have long been run on standard computers, as well as on specialized processors called digital signal processors, and on purpose-built hardware such as application-specific integrated circuit (ASICs). Currently, there are additional technologies used for digital signal processing including more powerful general purpose microprocessors, field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), digital signal controllers (mostly for industrial applications such as motor control), and stream processors, among others.
Digital signal processing can involve linear or nonlinear operations. Nonlinear signal processing is closely related to nonlinear system identification and can be implemented in the time, frequency, and spatio-temporal domains.
Signal sampling
Main article: Sampling (signal processing)
The increasing use of computers has resulted in the increased use of, and need for, digital signal processing. To digitally analyze and manipulate an analog signal, it must be digitized with an analog-to-digital converter. Sampling is usually carried out in two stages, discretization and quantization. In the discretization stage, the space of signals is partitioned into equivalence classes and quantization is carried out by replacing the signal with representative signal of the corresponding equivalence class. In the quantization stage, the representative signal values are approximated by values from a finite set.
The Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem states that a signal can be exactly reconstructed from its samples if the sampling frequency is greater than twice the highest frequency of the signal, but this requires an infinite number of samples. In practice, the sampling frequency is often significantly higher than twice that required by the signal's limited bandwidth.
Some (continuous-time) periodic signals become non-periodic after sampling, and some non-periodic signals become periodic after sampling. In general, for a periodic signal with period T to be periodic (with period N) after sampling with sampling interval Ts, the following must be satisfied:
where k is an integer.
DSP domains
In DSP, engineers usually study digital signals in one of the following domains: time domain (one-dimensional signals), spatial domain (multidimensional signals), frequency domain, and wavelet domains. They choose the domain in which to process a signal by making an informed assumption (or by trying different possibilities) as to which domain best represents the essential characteristics of the signal. A sequence of samples from a measuring device produces a temporal or spatial domain representation, whereas a discrete Fourier transform produces the frequency domain information, that is, the frequency spectrum. Autocorrelation is defined as the cross-correlation of the signal with itself over varying intervals of time or space.
Time and space domains
Main article: Time domain
The most common processing approach in the time or space domain is enhancement of the input signal through a method called filtering. Digital filtering generally consists of some linear transformation of a number of surrounding samples around the current sample of the input or output signal. There are various ways to characterize filters; for example:
- A "linear" filter is a linear transformation of input samples; other filters are "non-linear". Linear filters satisfy the superposition condition, i.e. if an input is a weighted linear combination of different signals, the output is a similarly weighted linear combination of the corresponding output signals.
- A "causal" filter uses only previous samples of the input or output signals; while a "non-causal" filter uses future input samples. A non-causal filter can usually be changed into a causal filter by adding a delay to it.
- A "time-invariant" filter has constant properties over time; other filters such as adaptive filters change in time.
- A "stable" filter produces an output that converges to a constant value with time, or remains bounded within a finite interval. An "unstable" filter can produce an output that grows without bounds, with bounded or even zero input.
- A "finite impulse response" (FIR) filter uses only the input signals, while an "infinite impulse response" filter (IIR) uses both the input signal and previous samples of the output signal. FIR filters are always stable, while IIR filters may be unstable.
A filter can be represented by a block diagram, which can then be used to derive a sample processing algorithm to implement the filter with hardware instructions. A filter may also be described as a difference equation, a collection of zeroes and poles or, if it is an FIR filter, an impulse response or step response.
The output of a linear digital filter to any given input may be calculated by convolving the input signal with the impulse response.
Frequency domain
Main article: Frequency domain
Signals are converted from time or space domain to the frequency domain usually through the Fourier transform. The Fourier transform converts the signal information to a magnitude and phase component of each frequency. Often the Fourier transform is converted to the power spectrum, which is the magnitude of each frequency component squared.
The most common purpose for analysis of signals in the frequency domain is analysis of signal properties. The engineer can study the spectrum to determine which frequencies are present in the input signal and which are missing.
In addition to frequency information, phase information is often needed. This can be obtained from the Fourier transform. With some applications, how the phase varies with frequency can be a significant consideration.
Filtering, particularly in non-realtime work can also be achieved by converting to the frequency domain, applying the filter and then converting back to the time domain. This is a fast, O(n log n) operation, and can give essentially any filter shape including excellent approximations to brickwall filters.
There are some commonly used frequency domain transformations. For example, the cepstrum converts a signal to the frequency domain through Fourier transform, takes the logarithm, then applies another Fourier transform. This emphasizes the harmonic structure of the original spectrum.
Frequency domain analysis is also called spectrum- or spectral analysis.
Z-plane analysis
Main article: Z-transform
Whereas analog filters are usually analyzed in terms of transfer functions in the s plane using Laplace transforms, digital filters are analyzed in the z plane in terms of Z-transforms. A digital filter may be described in the z plane by its characteristic collection of zeroes and poles. The z plane provides a means for mapping digital frequency (samples/second) to real and imaginary z components, where for continuous periodic signals and ( is the digital frequency). This is useful for providing a visualization of the frequency response of a digital system or signal.
Wavelet
Main article: Discrete wavelet transform
An example of the 2D discrete wavelet transform that is used in JPEG2000. The original image is high-pass filtered, yielding the three large images, each describing local changes in brightness (details) in the original image. It is then low-pass filtered and downscaled, yielding an approximation image; this image is high-pass filtered to produce the three smaller detail images, and low-pass filtered to produce the final approximation image in the upper-left.
In numerical analysis and functional analysis, a discrete wavelet transform (DWT) is any wavelet transform for which the wavelets are discretely sampled. As with other wavelet transforms, a key advantage it has over Fourier transforms is temporal resolution: it captures both frequency and location information (location in time).
Applications
The main applications of DSP are audio signal processing, audio compression, digital image processing, video compression, speech processing, speech recognition, digital communications, radar, sonar, financial signal processing, seismology and biomedicine. Specific examples are speech compression and transmission in digital mobile phones, room correction of sound in hi-fi and sound reinforcement applications, weather forecasting, economic forecasting, seismic data processing, analysis and control of industrial processes, medical imaging such as CAT scans and MRI, MP3 compression, computer graphics, image manipulation, hi-fi loudspeaker crossovers and equalization, and audio effects for use with electric guitar amplifiers.
Implementation
Depending on the requirements of the application, digital signal processing tasks can be implemented on general purpose computers.
Often when the processing requirement is not real-time, processing is economically done with an existing general-purpose computer and the signal data (either input or output) exists in data files. This is essentially no different from any other data processing, except DSP mathematical techniques (such as the FFT) are used, and the sampled data is usually assumed to be uniformly sampled in time or space. For example: processing digital photographs with software such as Photoshop.
However, when the application requirement is real-time, DSP is often implemented using specialized microprocessors such as the DSP56000, the TMS320, or the SHARC. These often process data using fixed-point arithmetic, though some more powerful versions use floating point. For faster applications FPGAs might be used. Beginning in 2007, multicore implementations of DSPs have started to emerge from companies including Freescale and Stream Processors, Inc. For faster applications with vast usage, ASICs might be designed specifically. For slow applications, a traditional slower processor such as a microcontroller may be adequate. Also a growing number of DSP applications are now being implemented on embedded systems using powerful PCs with multi-core processors.